Life-Empore was focus on the study of the following emerging pollutants previously selected because of their presence in water bodies (and wide use in Europe) as well as their environmental risks. The emerging pollutants selected are the following:
Chlorpyrifos
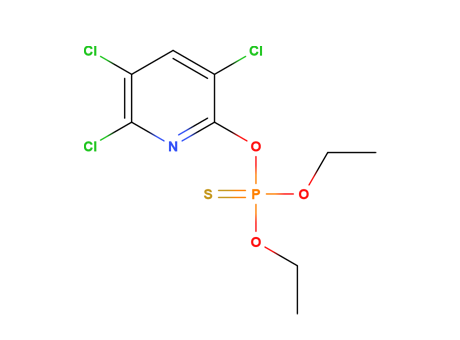
MAIN USE
Pesticide. It has been widely used in homes and farms. At homes, it is used to control cockroaches, fleas and termites; it is also used in some pet flea and tick collars. At farms, it is used to control ticks on cattle and as a spray to control crop pests.
PROBLEMA AMBIENTAL
It is moderately toxic, and chronic exposure has been linked to neurological effects, developmental disorders and autoimmune disorders.
Trifluralin
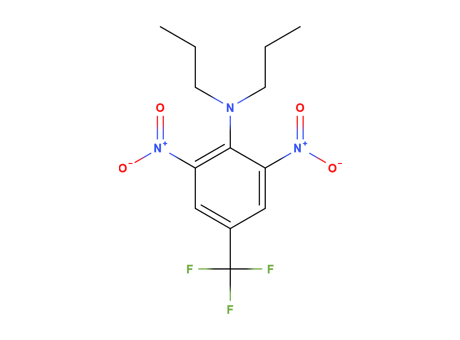
MAIN USE
LaTrifuralin is a commonly used pre-emergence herbicide. Trifuralin is generally applied to the soil to provide control of a variety of annual grass and broadleaf weed species. It inhibits root development by interrupting mitosis, so it can control weeds as they germinate.
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK
It is transiently transformed into many different products as it degrades finally being incorporated into soil-bound residues or converted to carbon dioxide (mineralized). Among the more unusual behaviors of tiflurain is inactivation in wet soils. This has been linked to transformation of the herbicide by reduced soil minerals, which in turn had been previously reduced by soil microorganisms as electron acceptors in the absence of oxigen. This environmental process has been reported for many structurally related herbicides (dinitroanilines) as well as a variety of energetic compounds (explosives).
4-t-OctylPhenol
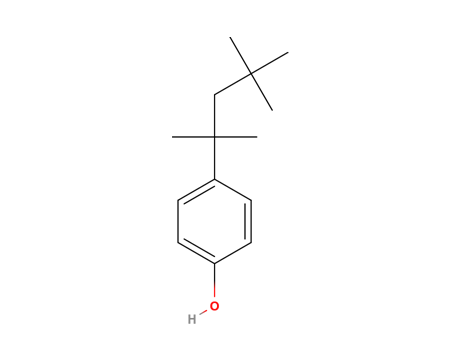
MAIN USE
The main areas of use area as intermediate in the production of phenol/formaldehyde resins and in the manufacture of octylphenol ethoxylates. These chemicals are used to in rubber, in pesticides and paints.
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK
It has a estrogenic effect at concentrations of 1-20 mg/L. They are also persistent and bioaccumulable. It has been proposed that a global decline in sperm counts, semen quality, and several male reproductive disorders are associated with exposure to environmental estrogenic chemicals. Recent studies, using pubertal male Wistar rats, demonstrated that Octylphenol can reduce sperm counts resulting from lowered plasma testosterone in male rats just after puberty.
Di (2-etilhexil) ftalato (DEHP)
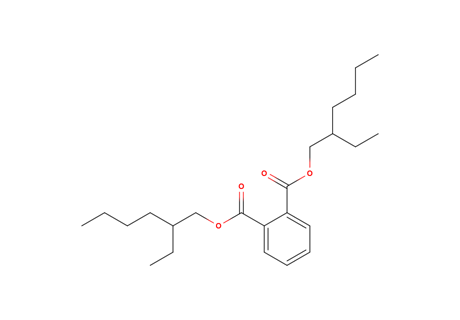
MAIN USE
It is mainly used as an intermediate in the production of polyvinylchloride (PVC), as well as in the production of etoxilat and octifenol. These products are presented in rubber, pesticides and paints.
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK
DEHP acts as androgen receptor agonists and antagonists and inhibits fetal steroidogenesis and it can induce reproductive malformations in humans and animals.
Diuron
MAIN USE
It is a commonly used herbicide and generally applied to the soil to provide control of a variety of annual grass.
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK
It is toxic compound for human beings, and chronic exposure has been linked to and mucous irritation. It is a well-known carcinogenic compound, toxic at the freatic lawyer level.
Diclofenac
MAIN USE
It is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), used to reduce inflammation, and as an analgesic reducing pain in certain conditions. It is sold under different trade names.
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK
Diclofenac causes acute toxicity and especially chronic toxicity in aquatic organisms, with long lasting harmful effects. It can also bioaccumulates by inducing toxicity along the trophic chains.
17alfa-Ethinyl Estradiol
MAIN USE
It is female hormone derived from 17b-estradiol (E2), the main estrogen in humans. It is used in the formulation of oral contraconceptive pills.
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK
Apparent feminization of male fish and subsequent collapse of a population, even at very low environmental concentrations. It acts as an endocrine disruptor. The endocrines disruptors are synthetic compounds or natural products excreted by human that can affect the endocrine system. Their effects are well-kwon, such a decrease in the fertility, growth and development and sexual alterations.
17 beta Estradiol
MAIN USE
It is a steroid and estrogen sex hormone, and the main female sex hormone, with an important role in the regulation of the menstrual female reproductive cycles. Estradiol is essential for the development and maintenance of female reproductive tissues but it also has important effects in many other tissues including bones.
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK
It acts as endocrine disruptor. The endocrines disruptors are synthetic compounds or natural products excreted by human that can affect the endocrine system. Their effects are well-kwon, such a decrease in the fertility, growth and development and sexual alterations.
Erythromycin
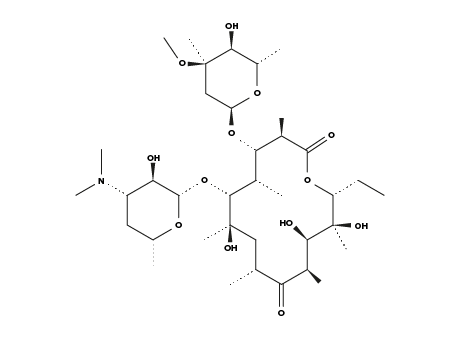
MAIN USE
Erythromycin is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes respiratory tract infections, skin infections, chlamydia infections, pelvic inflammatory disease and syphilis.
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK
Antibiotics can affect bacteria populations which are living in the water bodies where they are discharged. As a result, resistant strains of bacteria are developed, making the antibiotic inefficient for its initial purpose.
Chloramphenicol
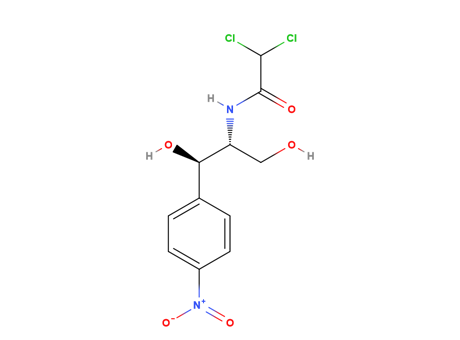
MAIN USE
It is an antibiotic useful for treating a high number of bacterial infections, including meningitis, plague, cholera and typhoid fever.
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK
Antibiotics can affect bacteria populations which are living in the water bodies where they are discharged. As a result, resistant strains of bacteria are developed, making the antibiotic inefficient for its initial purpose.
Carbamazepine
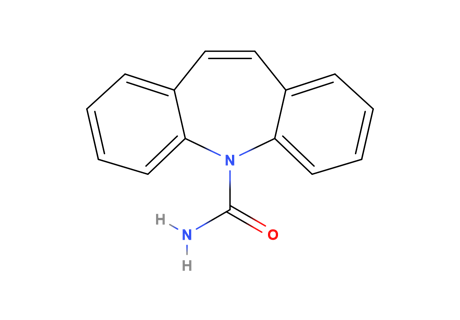
MAIN USE
It is a medication used primarily in the treatment of epilepsy and neuropathic pain. It may be used in schizophrenia along with other medications and as a second line agent in bipolar disorder.
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK
It can induce bioaccumulation fishes, disorder the behavior and physiology of insects and inhibit the growth of aquatic plants and algae. Halogenated compound characteristic for its low biodegradability and its tendency in be accumulated in sludges of WWTPs as a result of its hydrophobicity.
2-(p-isobutilfenil) propionic acid
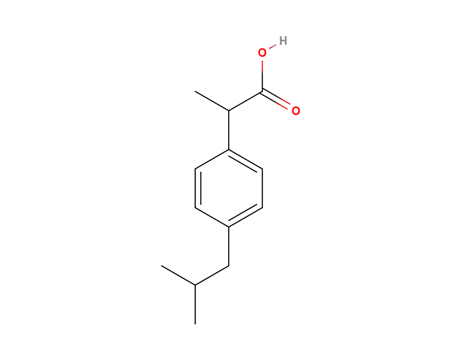
MAIN USE
It is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used for relieving pain, helping with fever and reducing inflammation. Ibuprofen might be considered a weaker anti-inflammatory than other NSAIDs.
PROBLEMA AMBIENTAL
It can affect the aquatic bodies as a result of its capacity of bioaccumulation and toxicity.
Fluoxetine hidrocloruro (Prozac)
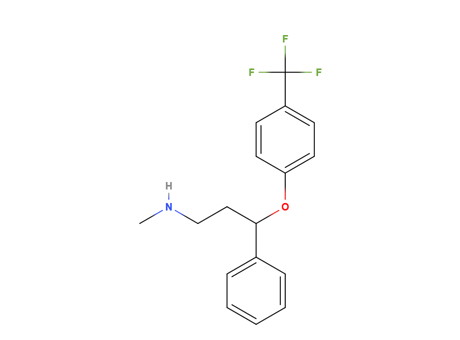
MAIN USE
It is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSR) class. Fluoxetine is used for the treatment of major depressive disorder (including pediatric depression), obsessive-compulsive disorder (in both adults and children), bulimia nervosa, panic disorder, and premenstrual dysphoric disorder.
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK
It can affect the aquatic bodies as a result of its toxicity.
Estrone
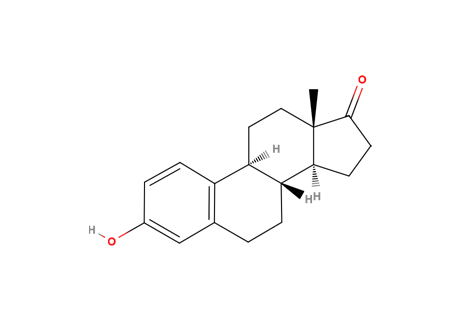
MAIN USE
It is an estrogenic hormone secreted by the ovary as well as adipose tissue. Estrone in one of several natural estrogens excreted with the urine and it is also used as antiovulatory.
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK
It acts as endocrine disruptor. The endocrines disrupts are synthetic compounds or natural products excreted by human that can affect the endocrine system. Their effects are well-known, such a decrease in the fertility, growth and development and sexual.
AMPA
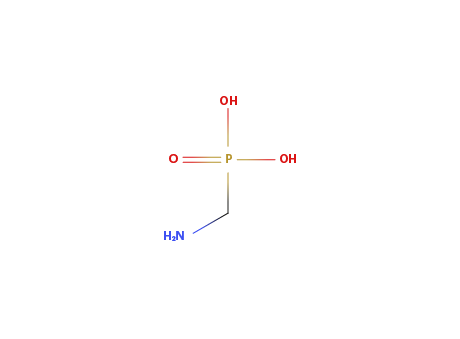
MAIN USE
Main herbicide glyphosate degradation compound.
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK
Toxicity similar to glyphosate.
Glyphosate
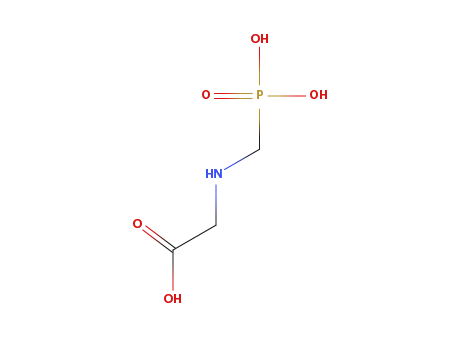
MAIN USE
Herbicide of common use.
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK
Possibly carcinogenic compound for humans.
Sulfathometoxazole
MAIN USE
It is an antibiotic useful for treating a high number of bacterial infections, mainly urine infections.
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK
Antibiotics can affect bacteria populations which are living in the water bodies where they are discharged. As a result, resistant strains of bacteria are developed, making the antibiotic inefficient for its initial purpose.
Ketoprofen
MAIN USE
It is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used for relieving pain, helping with fever and reducing inflammation.
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK
It can affect the aquatic bodies as a result of its capacity of bioaccumulation and toxicity.
Estriol
MAIN USE
Estriol is a metabolite of estradiol. It belongs to the category of sex hormones, subcategory of estrogen.
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK
It acts as endocrine disruptor. The endocrines disrupt are synthetic compounds or natural products excreted by human that can affect the endocrine system. Their effects are well-known, such a decrease in the fertility, growth and development and sexual.
Are you an Associated Beneficiary? Access private area to download documents Private zone